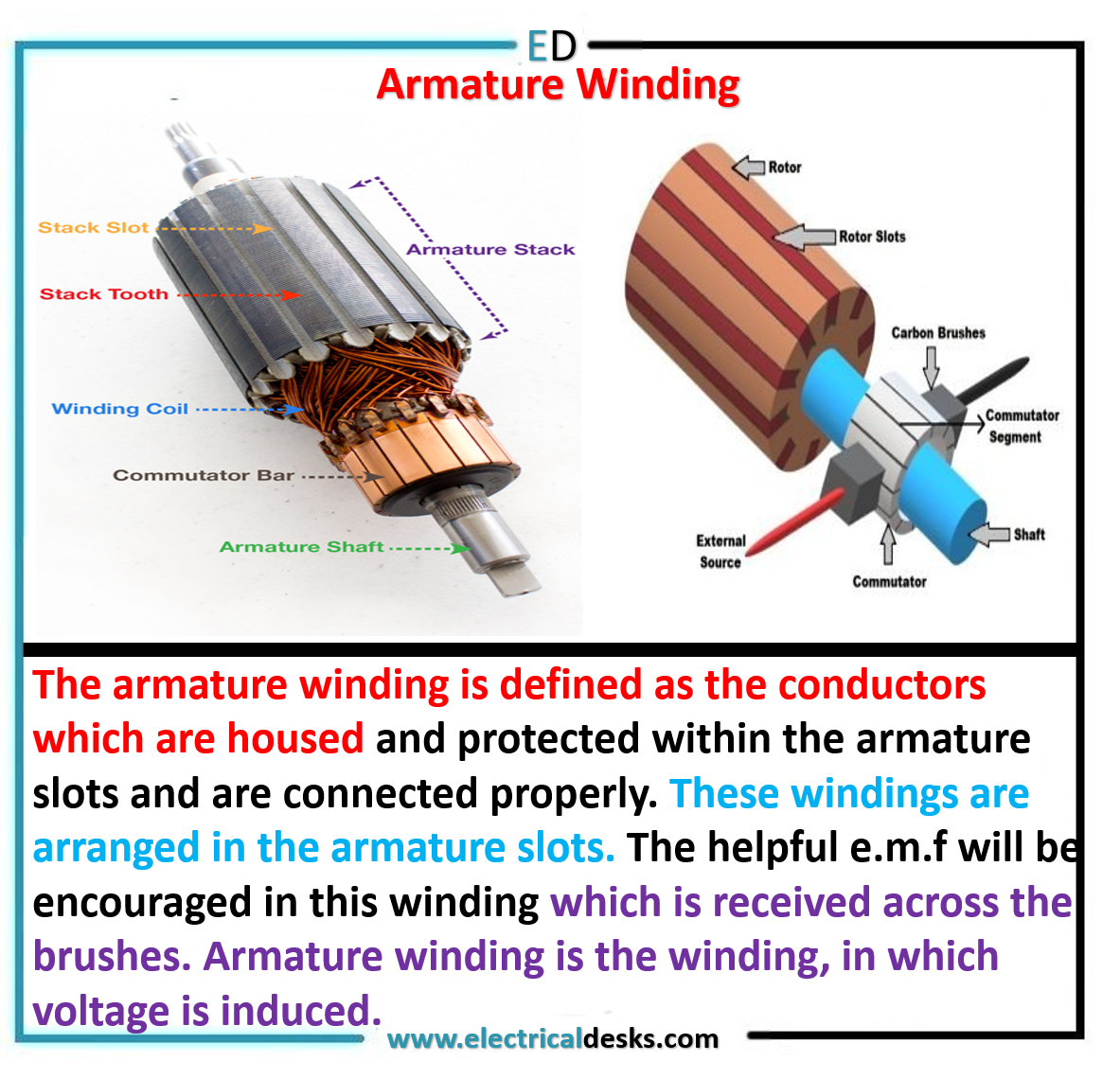
What is Armature winding?
The insulated copper or aluminium conductors are housed in armature slots is called armature winding.
The armature winding is the most crucial part of rotating electrical machines. There are two functions of armature winding. 1. The mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy which takes place in the generator and 2. The electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy which takes place in the motor. The armature winding is divided into two types
1. Lap Winding
2. Wave Winding
The lap winding is further classified into three types
1. Simplex lap winding
2. duplex lap winding
3. Triplex lap winding
Lap Winding
The end of each armature coil is connected to the adjacent segment on the commutator is called lap winding. In lap winding, armature coils lap back to the succeeding coils on the commutator. The lap winding is also called parallel winding or multiple winding. The emf produced by the lap winding is less as compared to the wave winding. so the efficiency of the lap winding is also less compared to the wave winding.
For the lap winding the number of parallel paths(A) is exactly equal to the number of poles(P).
Number of parallel paths(A) = Number of poles(P)
The meaning of a parallel path is a total number of paths by which the current will flow between the terminals. it is denoted by the 'A'.
In lap winding, the number of brushes required is equal to the number of parallel paths. These carbon brushes are divided into negative and positive polarity.
The lap winding is useful for low voltage and high current applications. Due to the existence of a large number of parallel paths in lap winding, the lap wound armature winding is capable of supplying larger load currents.
Types of the lap winding
1. Simplex lap winding
A winding in which the number of poles is equal to the number of parallel paths between the carbon brushes is called simplex lap winding.
This type of winding is obtained by placing the one winding on the armature slots. In simplex lap winding one parallel path is in the N pole and one parallel path is in the S pole.
In simplex lap winding coil starts from the commutator segment 1 and after one turns, the coil ends at commutator segment 2 and then the second coil starts.
Number of parallel path(A) = P (Number of Poles)
2. Duplex Lap Winding
A Winding in which the number of the parallel path between the carbon brushes is twice the number of poles is called duplex lap winding. The duplex lap winding is used for high current applications.
The duplex lap winding is made by placing two similar coils on the same armature slots and connecting an even number commutator bar to the one winding and an odd number of commutator bar to the second winding.
In duplex lap winding coil starts from the commutator segment 1 and after two turns, the coil ends at commutator segment 2 and then the second coil starts.
Number of parallel path(A) = 2P (Number of Poles)
In duplex lap winding, two parallel paths are in the N pole and two parallel paths are in the S pole.
3. Triplex lap winding
A winding which is connected to one-third of commutator bars is called triplex lap winding. A winding in which a number of parallel paths between the brushes are thrice the number of poles.
In triplex lap winding coil starts from the commutator segment 1 and after three turns, the coil ends at commutator segment 2 and then the second coil starts.
This type of windings is used for higher and larger current applications. These winding coils are very costly.
Number of parallel path(A) = 3P (Number of Poles)
Advantages of lap winding
1. The lap windings are used for large current applications because lap winding has more parallel paths.
2. The lap winding is used for low voltage and high current generators.
Disadvantages of lap winding
1. The emf produced by the lap winding is less as compared to the wave winding. For producing the same emf more conductors are required. so the cost of the winding increased.
2. The efficiency of the lap winding is less as compared to the wave windings.