What are overhead line insulators and their function?
- The overhead line conductors are bare and not covered with insulating material.
- The bare conductors are insulated from the earth and also from the line support with help of insulators.
- The bare line conductors are supported on the insulators.
- There is no current leakage in the insulator through support.
- The insulators are mounted on the cross arms and phase conductors are attached to the insulators.
- The Insulators provide insulation to the conductors and also provide clearance between the conductors and line supports.
- The insulators prevent short-circuiting between the different phases and provide mechanical support to the phase conductors.
Important properties of overhead line insulators
- The insulators should have high mechanical strength to withstand the conductor weight, wind, and ice force.
- The insulators should have high relative permittivity, so the insulator provides high dielectric strength.
- To prevent leakage current, insulators should have high insulation resistance.
- The insulators should have high ratio a of rupture strength to flashover voltage.
- The insulators should have to ability to withstand large temperature variations.
Types of insulators
1. Pin Type Insulators
2. Suspension Type Insulators
1. Hewlett or Interlinking Type Suspension Insulators
2. Cemented-Cap Type Suspension Insulators
3. Core and Link Type Suspension Insulators
3. Strain Insulators
4. Post Insulators
5. Shackle Insulators
6. Stay Insulators
1. Pin Insulators
- The pin insulators are used for busbar and conductor support voltage up to 33KV.
- The pin-type insulators have a long life of about 50 years.
- The Pin-type insulators are made from porcelain or toughened glass, ceramic, silicon rubber, and polymer.
- The pin type insulator is designed on a pin and the pin is fitted on the cross arms of the line support.
- The Pin type insulator is screwed on the pin and the phase conductor is placed in the groove at the top of the pin insulators.
- The conductor is tied down with the help of soft copper or soft aluminum biding wire according to the phase conductor material.
- The Pin insulator consists of a metal pin, porcelain insulator disc, and lead thimble.
- The lead thimble is employed to avoid direct contact between the porcelain and metal pin.
- The pin insulator should be mechanically strong to withstand the force due to the weight of the conductor, ice loading, and wind pressure.
- For lower voltages single piece type and for higher transmission voltages stronger pin type insulators are used. here pieces are called petticoats or rain sheds.
- The flashover voltage between the conductor and insulator pin is increased by increasing the rain shed which increases the adequate length of the leakage path.
- The rain sheds or petticoats are designed in such a way that when the outer surface is wet due to rain, sufficient leakage resistance is provided by the inner dry surface.
- The single-piece insulator is used for voltage up to 11kv and for higher voltages, a multiple-piece pin insulator is used.
- The multiple-piece pin insulator is more advantages than the single-piece pin insulator because defects in the one piece do not seriously affect the mechanical strength of the insulator.
- One piece faulty pin insulator working properly at normal voltage until the defective unit was traced and replaced.
- In rural 11kv electrical lines have less load and so use light load conductors. so in rural electrification single-piece insulators are employed for economic purposes.
- For urban 11kv feeders, which supply load too heavily loaded industrial feeders and multiple piece insulators are preferred which are more reliable.
- The flash over distance is less in the case of wet insulators as compared to dry insulators.
- The pin-type insulator is used on an intermediate pole on a pin-type straight run.
- The safety factor( Ration of spark over voltage to working voltage) for pin type insulator is 10.
- The surface leakage current in pin-type insulators on the surface is due to the accumulation of dirt.
Advantages of Pin Insulators
- The Pin insulators are cheaper in cost.
- The Pin insulator shorter line pole to give the same conductor clearance above the ground. The pin insulators are raises the conductor above the cross arms. The suspension insulator suspends the conductor below the cross arms.
- The Pin insulator has high mechanical strength to withstand the weight of the conductor, wind, and ice loading.
- The pin insulator has good creepage(more distance between two conductive parts) distance due to rain sheds or petticoats type design.
- The construction of the pin-type insulators is very simple and maintenance is also easy.
- The Pin type insulator is used vertically as well as horizontally in line supports.
Disadvantages
- The pin insulator becomes bulky when designed for higher voltages.
- The Pin insulator becomes uneconomical when used for higher voltage.
- The pin-type insulators are not used beyond 33kv.
- The Pin type insulator is used only for distribution purpose suspension-type and not used for transmission purposes.
2. Suspension Type Insulators
- The suspension-type insulators consist of a number of porcelain or silicon rubber discs that are connected in series with help of metal links or FRP rods in the form of string.
- The suspension insulator is hung below the cross arms of the supporting pole and the line conductor are attached below the suspension insulator's lower end.
- In a suspension insulator, there is no pin problem so we can put any distance between the cross arms and conductor by adding the number of disc.
- The entire unit of the suspension insulator is called a suspension string.
- The number of discs used in the suspension insulator depends upon the working voltage, weather conditions, type of transmission construction, and size of the insulator used.
There are three types of suspension insulators
- Hewlett or Interlinking Type Suspension Insulators
- Cemented-Cap Type Suspension Insulators
- Core and Link Type Suspension Insulators
1. Hewlett or Interlinking Type Suspension Insulators
- In this type of insulator, each disc consists of one piece of porcelain, and a central bulbous portion is provided with two curved tunnels which are lying in planes at right angles to each other.
- The short steel strips form the connection between the individual porcelain discs and steel strips are treaded through the tunnels.
- The loop through each other discs is separated by the porcelain.
- Due to high electrostatics between the metal links, these types of insulators are more punctured than other types of insulators.
2. Cemented-Cap Type Suspension Insulators
- These insulators consist of porcelain discs that are grooved at the bottom to increase the surface leakage path.
- The top of the insulator is cemented galvanized iron make cap which is hung on cross arms.
- The galvanized steel pin is threaded or cemented below hollow cavity porcelain discs.
- The lower enlarged end of the steel pin is fitted on the cavity of the steel cap of another suspension insulator and forms a ball and socket connection.
- Due to different coefficients of expansions of cement, steel, and porcelain and no provision is made for their expansion. When the temperature changes occur it cracks the porcelain and leads to electrical failure.
3. Core and Link Type Suspension Insulators
- In these types of insulators, each disc is symmetrically placed and it conforms to the electrostatic lines of force.
- The metal work in these types of insulators consists of pressed steel spiders, the leg of steel spiders are fastened into the porcelain by alloy.
- The metal works and porcelain have the same coefficient of expansion. so the failure of insulators due to the temperature variation is reduced in these types of insulators.
- These types of insulators have a high puncture strength.
Advantages of Suspension insulators
- The suspension type insulator is cheaper in cost and used for very high voltages.
- Each unit or disc is designed for low voltages (11kv) and can be used by connecting them in series depending upon the working voltage.
- In the event of failure of the suspension insulator, only one faulty disc is replaced instead of the whole string.
- The suspension insulator gives more flexibility to the transmission line and also mechanical stresses are reduced. The insulator string is free to swing in any direction in suspension type insulators.
- If the load of the transmission line increased then the increased demand of the line can be met by increasing the voltage of the transmission line by adding another set of conductors and adding one or more sets of discs in the insulator string.
- In the case of long spans in the river, valley crossing where heavy conductor load is to be sustained, two-disc insulator strings are used which is called bridling.
- If the suspension insulator is used with the steel tower, the line conductor is less affected by the lightning stroke because every conductor is hung below the earth wire on cross arms. The transmission tower works as a lightning rod.
Disadvantages of Suspension Insulators
- In suspension insulators, large spacing between the conductor is required.
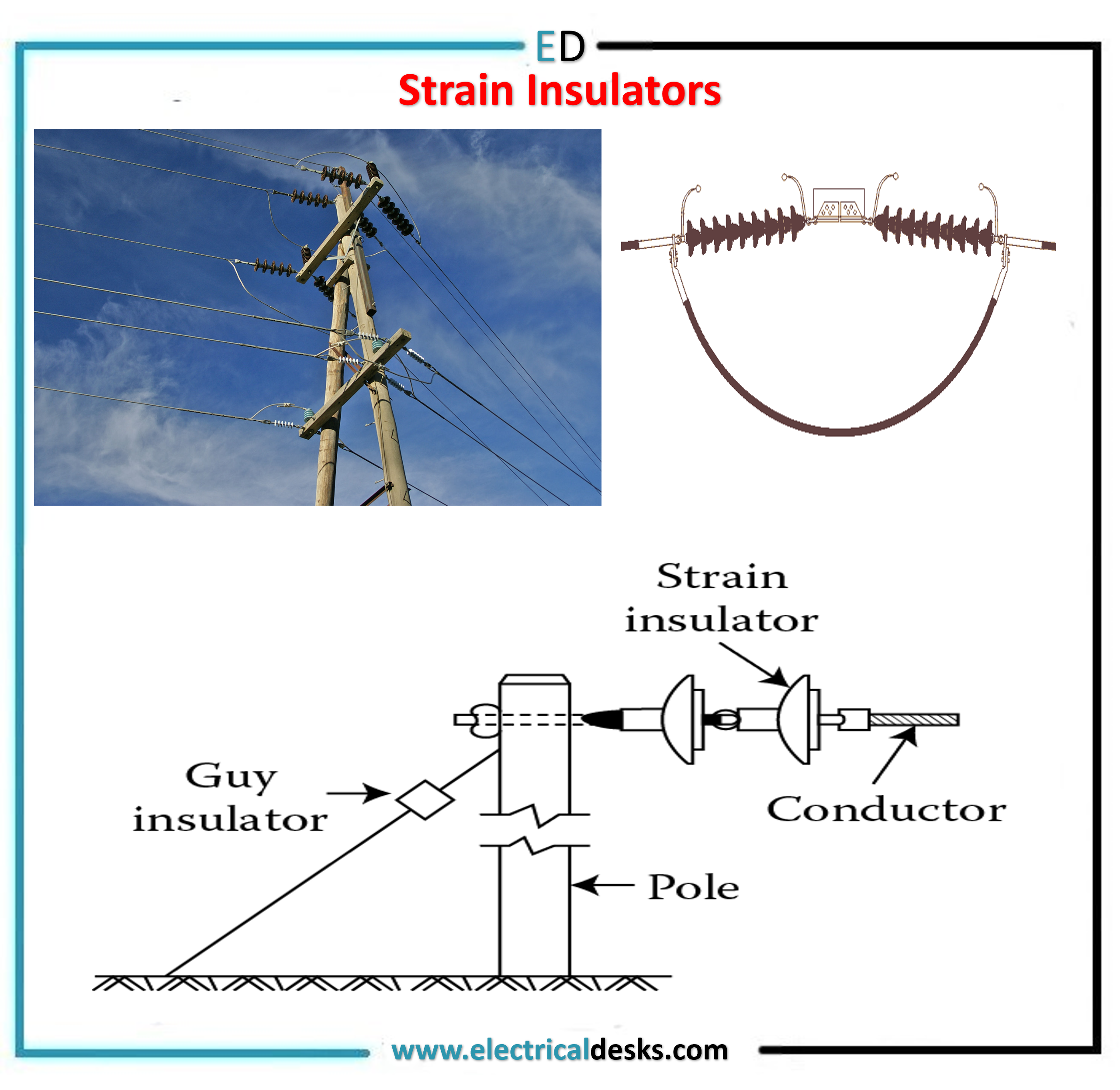
3. Strain Insulators
- When there is a dead end of the line or the line has a sharp curve or corner, the line crosses the valley or river, or the line is subjected to greater tension, where strain-type insulators are used.
- For higher voltage transmission line strain type insulators consisting assembly of suspension type insulators is used.
- The strain insulators should have high dielectric properties and high mechanical strength.
- Where the tension is increased high, at river crossing spans, two to four strings of insulators in parallel are used.
- The discs of strain insulators are employed in the vertical plane.
- The strain insulator is also called a tension insulator.
4. Post Insulators
- The post insulators are used for supporting the bus bars and isolating switches.
- The Post insulator is the same as the pin insulator but the post insulator has a metal base with a metal cap so more than one unit can be mounted in series.
- The post insulator is a solid core insulator made from resin or porcelain.
5. Shackle Insulators
- The shackle insulators are also called spool-type insulators that are used for low voltage distribution lines.
- The shackle insulators provide a very neat, efficient, and economical arrangement.
- Every insulator is coated with an extremely hard, smooth glaze that reduces the accumulation of surface dirt.
- The wet flashover voltage of the shackle insulator is 10kv and the dry flashover voltage of the shackle insulator is 25kv.
- The puncture voltage of the shackle insulator is 35kv.
- The operating voltage of the shackle insulator is 1000v.
- The tapered hole in the shackle insulator distributes the load equally and reduces the possibility of breakage when the shackle insulator is heavily loaded.
- The shackle insulator is mounted horizontally or vertically and line conductors are fixed on the grooves with help of aluminum or copper binding material.
- The shackle insulator is used in all positions either intermediate, terminal, or angle.
- When the angle in the distribution line exceeds 60 deviations, shackle insulators are used in conjunction with the shackle straps.
6. Stay Insulators
- The stay insulators are in egg shape.
- The stay insulator is also called strain or guy insulator.
- The stay insulators are used in guy cables, where it is important to insulate the lower part of the guy cable from the pole for the safety of animals and people on the ground.
- The stay insulator consists of porcelain pieces drilled with two holes that are right angle to each other.
- The guy wires looped at two ends of stay insulators.
- The stay insulators are provided at a height of 3 meters from the ground level.
- The size of the stay insulator long or small used depends upon the tensile strength of the guy wire.