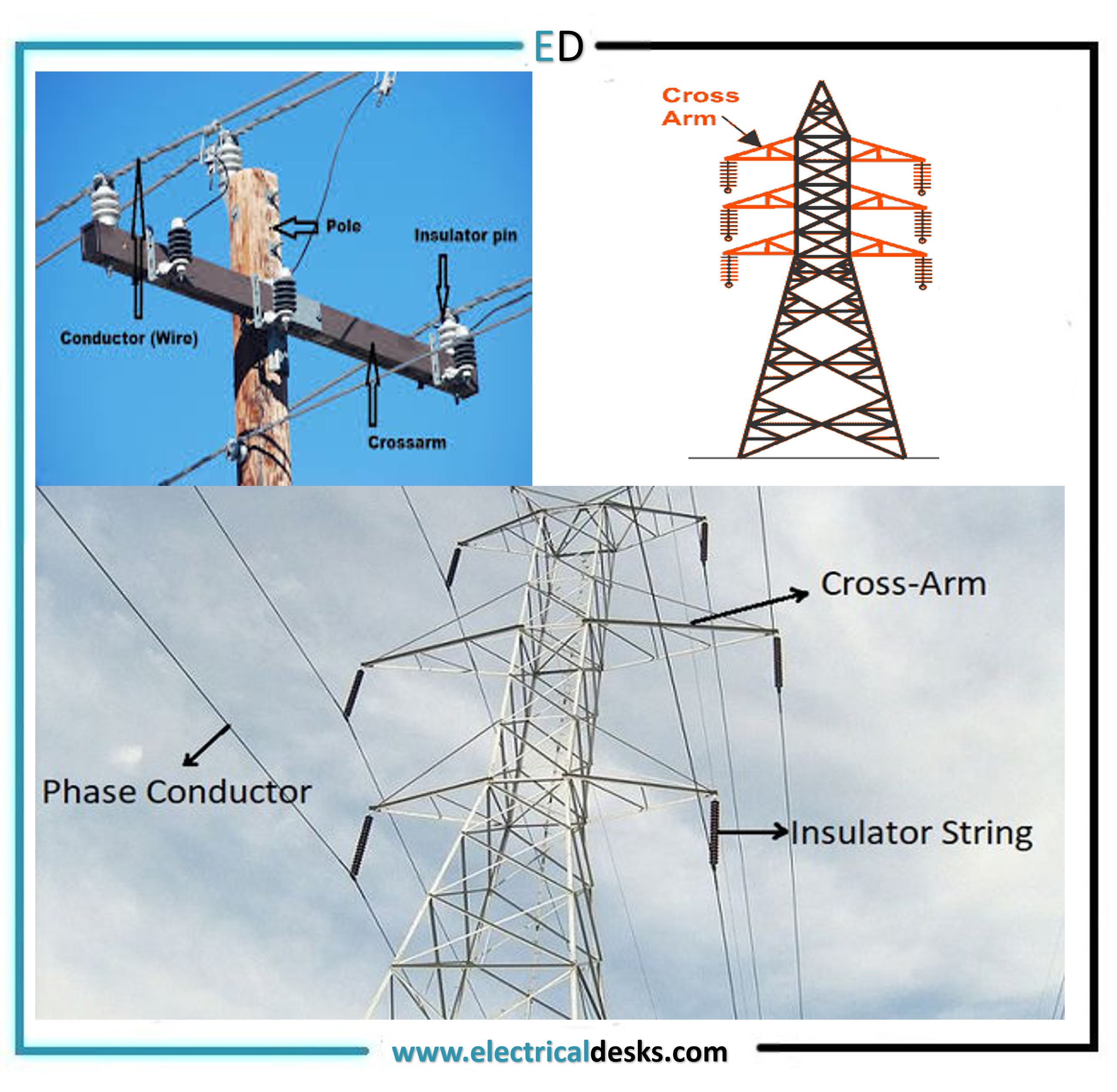
The Parts of the Distribution poles
1. Supports2. Cross arms and clamps
3. Insulators
4. Conductors
5. Guys and stays wire
6. Lightning arrester
7. Fuses and isolating switches
8. Earth Wire
9. Vee guards
10. Guard wire
11. Phase plates
12. Bird guards
13. Danger Plate
14. Barbed Wire
15. Vibration Damper
16. Top hampers
17. Jumpers
18. Repair sleeve
19. Midspan joint
Parts of the Transmission Tower
1. The peak portion of the transmission tower
2. The cage of the transmission tower
3. Cross Arm of transmission tower
4. Transmission Tower body
5. Boom of the transmission tower
6. Leg of the transmission tower
7. Stub-anchor bolt-base plate of transmission tower
8. Tension hardware of the transmission tower
9. Suspension hardware of the transmission tower
The Parts of the Distribution poles
1. Line Supports
- The main function of line support is to support the line live conductor and provide a suitable distance from the ground level.
- The various types of poles and towers are used as line supports depending upon the working voltage and region where these poles or towers are used.
- The Line supports can carry the load of the conductor, insulators, wind load on the conductors, and wind load on the line support themselves.
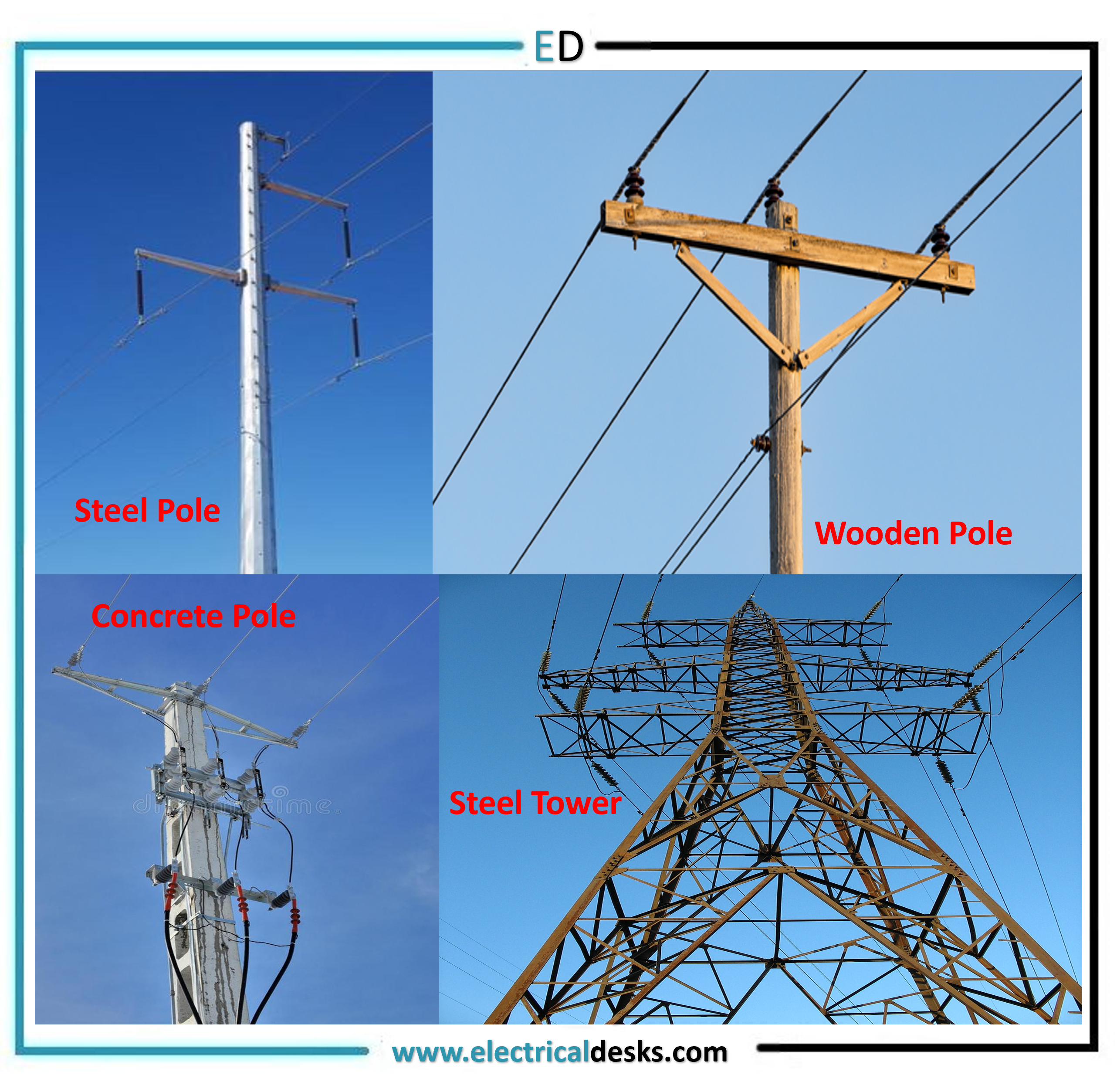
The various types of line supports are
1. Steel poles
2. Wooden poles
3. RCC poles
4. Steel towers
2. Cross arms and clamps
- The cross arms and clamps are used to support the conductor and insulators.
- The clamps are made from flat iron and used for fixing stay wire, earth wire, cross arms, and shackle insulators.
- The cross arms are made from galvanized steel.
- The main function of cross arms is to keep the phase conductor at the safest distance from each other and from the line support.
- The cross arms are cross pieces fitted at the top end of the line support with the help of a cross bracket.
- The cross bracket is used to support line insulators.
- The steel cross arms are mechanically stronger and used for the steel poles.
- The cross arms can withstand the forces caused by the insulators, their pins, conductor weight, and dead weight of insulator attachment.
3. Insulators
- The overhead line conductors are bare and not covered with insulating material.
- The bare conductors are insulated from the earth and also from the line support with help of insulators.
- The bare line conductors are supported on the insulators.
- There is no current leakage in the insulator through support.
- The insulators are mounted on the cross arms and phase conductors are attached to the insulators.
- The Insulators provide insulation to the conductors and also provide clearance between the conductors and line supports.
- The insulators prevent short-circuiting between the different phases and provide mechanical support to the phase conductors.
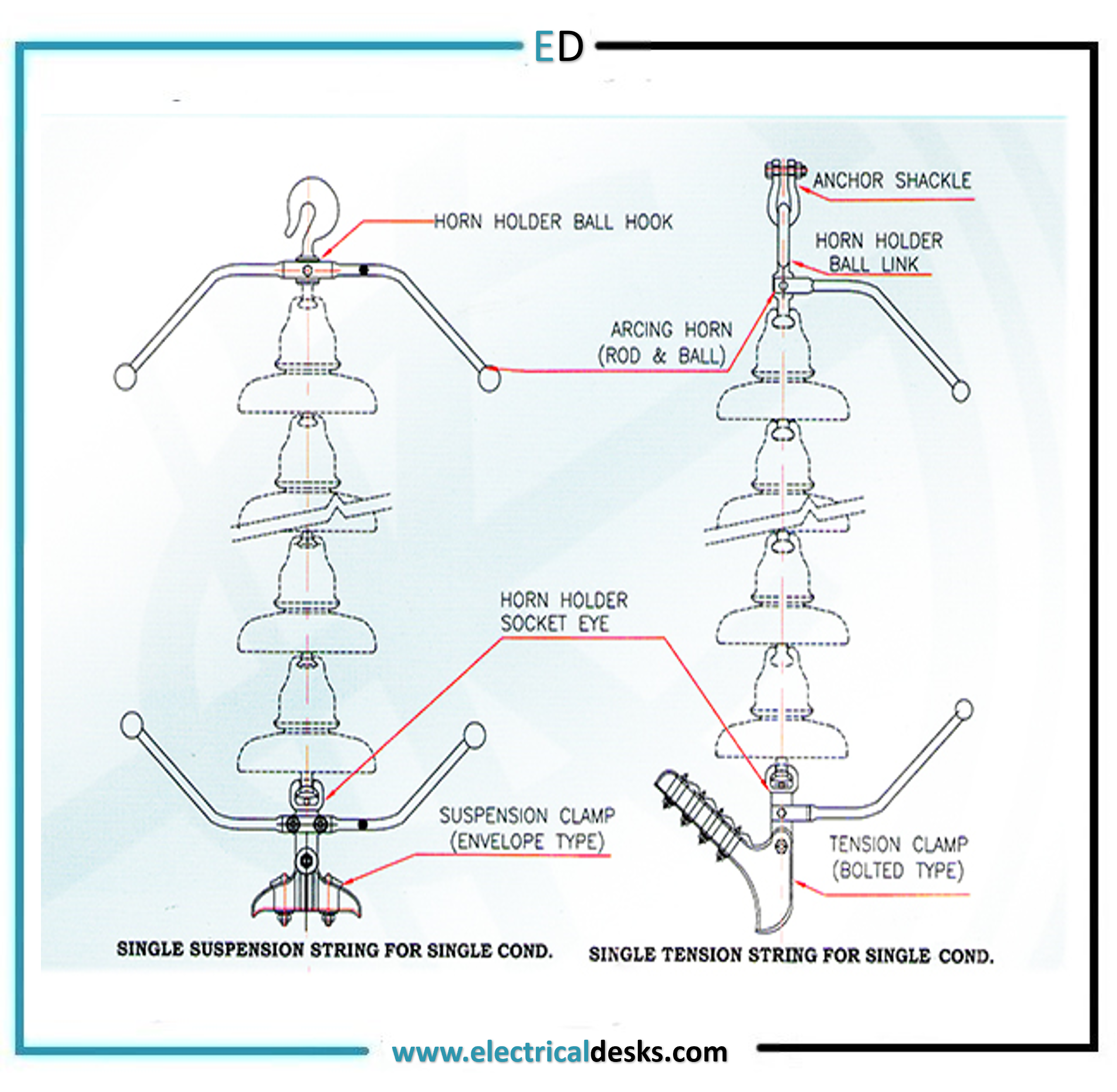
Types of insulators
1. Pin Type Insulators
2. Suspension Type Insulators
1. Hewlett or Interlinking Type Suspension Insulators
2. Cemented-Cap Type Suspension Insulators
3. Core and Link Type Suspension Insulators
3. Strain Insulators
4. Post Insulators
5. Shackle Insulators
6. Stay Insulators
4. Conductors
- The copper, aluminum, or aluminum conductors steel reinforcement conductors are used for power transmission from one location to another location depending upon the current carrying capacity and span of the line.
- The conductor is the heart of the transmission line and is the main component of the transmission system.
- The cost of the conductor material accounts for a major part of the total cost.
5. Guys and stays wire
- It is become essential to provide the stays and guy wire to the overhead distribution line at the distribution line's angle and terminal positions.
- At the line's angle and terminal positions, poles take the pull due to the weight and tension of conductors.
- The parts of guys are MS stay rod, MS stay bow, Thimble, stay insulator, guy wire, and stay clamp.
- The angle between the stay and pole should be between 60 to 45 degrees.
- The guy wires are galvanized steel wires and are usually of stranded sections.
- The tensile strength of the stay or guy wire is 7 tons/cm2.
6. Lightning arrester
- The lightning arrester is a protective device that is used to discharge higher voltages to the earth which is produced upon the transmission line due to the lightning.
- The lightning arrester diverts the very high voltages to the earth without affecting the continuity of supply.
- The lightning arresters are provided at top of the distribution poles.
7. Fuses and isolating switches
- The isolating switches are manually operated switches that isolate the circuit from the main power.
- The fuse is a protective device that is used to protect the electrical devices from excessive current and also prevent the short circuit in the system.
- The fuses and isolating switches are provided on the distribution poles for easy and safe distribution of electrical power.
8. Earth Wire
- The earth wire or shield wire is a bare conductor that is provided at the top of the transmission line and the earth wire offers a shield to the transmission line. The transmission towers are earthed at regular intervals.
- The earth wires intercept the lightning stroke before it hit the conductor of the transmission line. The earth wire protects transmission line equipment from damage due to lightning surges.
9. Vee guards
- The Vee guards are provided below the distribution lines conductor.
- The Vee guards are used to provide public safety on roads or streets.
- If a short circuit fault occurs in the distribution line and the bare live conductor is broken and fall down. These live conductors are guarded by the V guards.
10. Guard wire
- The guard wire is provided below and above the transmission line or distribution line.
- The guard wires are provided when communication lines are crossing the transmission lines or distribution lines.
- The guard wires are solidly connected to the earth.
11. Phase plates
- The phase plates are used for the identification of phases of transmission lines i.e. R phase means red color; the Y phase means yellow, and the B phase means blue color.
- These phase identification plates are provided on the transmission tower.
- These phase plates are made from excellent-quality raw materials.
- The phase plates last very long and phase plates are very strong and tensile.
12. Bird guards
- When birds sit on transmission towers' cross arms, they get electrocuted and short-circuited, causing transmission tripping.
- To reduce the unwanted tripping of transmission lines and save birds, bird guards are provided at top of cross arms so birds cannot sit on the cross arms.
13. Danger Plate
- Danger plates are used for indicating danger in the transmission.
- The danger slogan is written on plates that this line has a heavy voltage.
- The danger plates are written in red color.
14. Barbed Wire
- Barbed wire is also known as an anticlimbing device.
- The barbed wire is wrapped around the transmission tower to protect the transmission tower against the climbing of unauthorized persons.
- Barbed wires are wrapped around the transmission towers at a height of 2.5m from the ground for at least 1 meter.
15. Vibration Damper
- The vibration damper absorbs aeolion vibration energy and prevents vibrations.
- The mostly used vibration damper is a stock bridge vibration damper in a transmission line to damp out the aeoline vibration.
- In the stock bridge vibration damper, 0.3m to 0.50m stranded cable was used. Two hollow weights are attached to either end. The vibration damper is attached to the conductor with help of a nut and bolt.
- The weights are made from galvanized.
16. Top hampers
- The top hampers are part of the transmission tower which supports the cross arm for the conductor.
17. Jumpers
- In the straight run, one tension pole is provided to facilitate the line sagging.
- The short-length conductor used for connecting one side of the line conductor to another side of the line conductor in a tension tower or pole is called a jumper.
- The jumper is made from the same material as a conductor is made and the jumper is having same current carrying capacity.
- The jumper beads are provided on a jumper to avoid birdcage.
18. Repair sleeve
- During the stringing work of the conductor, if the conductor is damaged due to some reason, then a repair sleeve is provided at the damaged portion.
- The repair sleeve is made from aluminum material for aluminum conductors.
19. Midspan joint
- The midspan joint is used for jointing the conductors.
Parts of the Transmission Tower
1. The peak portion of the transmission tower
- The portion above the cross arm is known as a peak to the transmission tower.
- The earth wire is provided at the top of the transmission tower to protect the transmission conductors from a direct lightning stroke.
2. The cage of the transmission tower
- The portion of the transmission tower between the tower body and the tower peak is known as a cage of the transmission tower.
- The tower cage holds the cross arms.
3. Cross Arm of transmission tower
- The cross arms are holding the conductor and insulators.
- The cross arm is the heart of the transmission tower.
- The cross arms provide sufficient clearance between the phase conductors.
- The size of the cross arms depends upon the transmission voltage, tower configuration, and minimum forming angle for stress distribution.
4. Transmission Tower body
- The portion between the below cross arm to the ground is known as the body of the transmission tower.
- This portion of the tower maintains the required ground clearance of the bottom conductor of the transmission line.
5. Boom of the transmission tower
- In transmission, the tower boom is a rectangular boom.
- In the transmission tower, the boom is connected to the lower body of the tower to support the power conductor mechanically.
6. Leg of the transmission tower
- The leg of the transmission tower is placed in concrete foundations and all four legs of the transmission tower are earthed to discharge the lightning surges and short circuit current.
7. Stub-anchor bolt-base plate of transmission tower
- The stub is made from concrete on the leg of the transmission towers to protect them from rusting due to water ingress on the leg of the transmission tower.
- The base plate is placed on concrete and the tower is constructed on it with help of an anchor bolt.
8. Tension hardware of the transmission tower
- The tension tower uses tension hardware to hold the conductor and insulator.
- The insulator used in the tension tower is 120KN.
- The tension hardware remains in vertical condition.
9. Suspension hardware of the transmission tower
- The suspension hardware is used in the suspension tower to hold the conductor and insulators.
- The insulator used in the suspension tower is 90KN.
- The suspension hardware remains in horizontal condition.