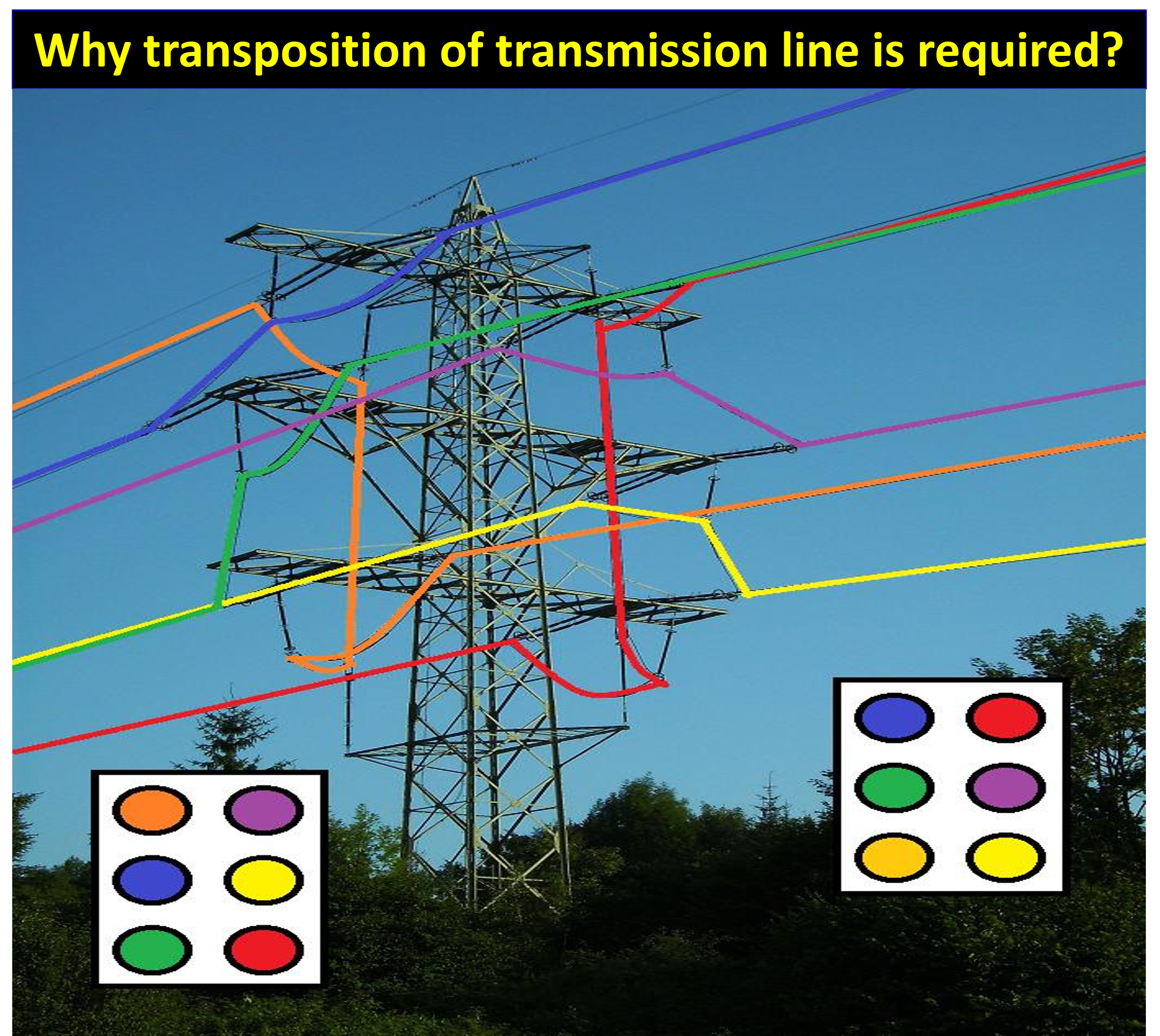
Transposition of transmission lines is necessary to reduce electrical interference and improve the efficiency of the line. When the wires in a transmission line are arranged in a certain way, they can produce electrical interference, which can affect the performance of nearby electronic devices. By transposing the wires, it is possible to minimize this interference.
Transposition is also used to balance the electrical load on the transmission line. When the load on a transmission line is not balanced, there can be losses due to the resistance of the wire. By transposing the wires, it is possible to evenly distribute the load, which can help to improve the efficiency of the line and reduce losses.
Transposition is typically done at switching stations and substations. At these locations, the conductors can be physically rotated to take up the next position in the regular sequence. This process equalizes the mutual inductance and capacitance between the lines, which helps to reduce electrical interference.
Unsymmetrical transmission lines, where the spacing between the conductors is irregular, can also cause problems. The complex value of inductances that results from this irregular spacing can make the study of power systems more complex. Transposition helps to reduce these effects by continually exchanging the position of the conductors. This helps to reduce the inducing voltages and magnetic fields that can cause interference in the line.